TL;DR — React SEO Checklist
Quick wins for React sites struggling with indexing or rankings:
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR)— Use Next.js, Remix, or custom SSR to serve HTML to crawlers
- Pre-rendering— Generate static HTML for public pages at build time
- Dynamic Rendering— Serve pre-rendered HTML to bots, client-side to users (last resort)
- Meta tags in
<head>— Use React Helmet or framework-native solutions - Structured Data— Add JSON-LD for rich results
- Core Web Vitals— Optimize LCP, CLS, INP (React hydration is often the culprit)
- URL structure— Use React Router with clean URLs, no hash routing
- Internal linking— Proper
<a href>tags, notonClicknavigation - Lazy loading— Code-split routes and components for faster FCP
React Rendering Strategies (Quick Reference)
| Strategy | Crawlability | Performance | Complexity | Best For |
| Client-Side (CSR) | ⚠️ Risky | Fast after JS loads | Low | Private dashboards |
| Server-Side (SSR) | ✅ Excellent | Slower server, fast FCP | Medium | Marketing pages, blogs |
| Static Generation (SSG) | ✅ Excellent | ⚡ Fastest | Low | Docs, landing pages |
| Incremental Static (ISR) | ✅ Excellent | ⚡ Fast + fresh | Medium | E-commerce, large sites |
| Dynamic Rendering | ✅ Good | Varies | High | Hybrid apps (fallback) |
Who this guide is for:SEO managers and developers working with React apps who need to ensure proper indexing, improve performance, and fix crawlability issues. Includes production-ready code for all major React frameworks.
Quick Start: Fix React SEO in 15 Minutes
Fast track for developers who need immediate results
Step 1: Verify Your Rendering Method (2 minutes)
# Check if your site uses SSR/SSG
curl -s https://yoursite.com | grep "<h1>"
# If you see your actual content → ✅ SSR/SSG working
# If you see empty <div id="root"></div> → ⚠️ CSR onlyAlternative:View source (Cmd+Option+U / Ctrl+U) in your browser. If content is visible → good. If empty → needs fixing.
Step 2: Choose Your Framework Path (5 minutes)
Option A: Already using Next.js?
# Ensure pages use getStaticProps or getServerSideProps
npx next build
npx next start
# Check source again - content should be thereOption B: Using Create React App?
# Quick migration to Next.js
npx create-next-app@latest my-app --typescript
# Copy components from src/ to new pages/
# Add getStaticProps to each pageOption C: Using Remix?
# Already SSR by default - just verify
npm run build
npm startStep 3: Add Essential Meta Tags (8 minutes)
For Next.js:
// pages/_app.js or app/layout.js
import Head from 'next/head'
export default function MyApp({ Component, pageProps }) {
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>Your Site Title</title>
<meta name="description" content="Your description" />
<link rel="canonical" href="https://yoursite.com" />
<meta property="og:title" content="Your Site Title" />
<meta property="og:description" content="Your description" />
</Head>
<Component {...pageProps} />
</>
)
}For Remix:
// app/routes/_index.tsx
export const meta: MetaFunction = () => {
return [
{ title: "Your Site Title" },
{ name: "description", content: "Your description" },
{ property: "og:title", content: "Your Site Title" },
];
};For CRA (temporary fix):
npm install react-helmet
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet'
function App() {
return (
<>
<Helmet>
<title>Your Site Title</title>
<meta name="description" content="Your description" />
</Helmet>
{/* Your app */}
</>
)
}✅ Done!Verify with:
- View source – see your content?
- Google Rich Results Test
- Submit sitemap to Google Search Console
Next steps:Continue reading for performance optimization, structured data, and advanced configurations.
Introduction
React is an excellent choice for building interactive user experiences, but its default client-side rendering (CSR) approach creates significant SEO challenges. When Google crawls a traditional React app, it sees an empty HTML shell—no content, no metadata, no links—until JavaScript executes.
While Googlebot can render JavaScript, relying on it creates risks:
- Delayed indexing— JS-rendered content enters a secondary indexing queue
- Wasted crawl budget— Googlebot must render pages twice (HTML fetch + JS execution)
- Missed content— Rendering failures or timeouts mean lost pages
- Poor Core Web Vitals— Heavy JS bundles, hydration delays, and layout shifts hurt rankings
This guide covers production-ready solutions for making React apps fully crawlable and performant, from framework choices to technical implementation details.
1. Understanding React’s SEO Challenges
The Client-Side Rendering Problem
Traditional React apps serve a minimal HTML skeleton:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My React App</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script src="/bundle.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Content only appears after JavaScript downloads, parses, and executes. For Googlebot, this means:
- Initial HTML fetch— Empty shell, no content
- Render queue— Page enters secondary queue for JS rendering
- JS execution— May take seconds, hours, or fail entirely
- Second indexing pass— Content finally available
Why This Matters for Rankings
Google has stated that JS-rendered content is indexed, but with caveats:
- Two-wave indexing— Initial HTML is indexed first, JS content later
- Rendering resources— Limited; not all pages get rendered
- Timeout issues— Complex apps may not finish rendering before timeout
- Mobile-first indexing— Slower devices may fail to render heavy apps
Real-world impact:Sites migrating from SSR to CSR often see 40–60% traffic drops due to indexing delays and lost rankings.
Google’s JS Rendering Reality
While Google claims to render JavaScript “well,” the reality is more nuanced:
- Rendering is not instant— Can take days or weeks for some pages
- Not all pages are rendered— Crawl budget constraints apply
- Bing and other engines— Far less capable at JS rendering
- Social media crawlers— Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn don’t render JS
2. Choosing the Right Rendering Strategy
Strategy Comparison
| Strategy | How It Works | SEO Impact | Use Cases |
| Client-Side Rendering (CSR) | Browser downloads JS, renders everything | ⚠️ Poor— Empty HTML, rendering delays | User dashboards, admin panels |
| Server-Side Rendering (SSR) | Server generates HTML for each request | ✅ Excellent— Full HTML immediately | Marketing sites, blogs, dynamic content |
| Static Site Generation (SSG) | Pre-render HTML at build time | ✅ Best— Fast, fully crawlable | Documentation, landing pages |
| Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR) | SSG + background updates | ✅ Excellent— Fast + fresh | E-commerce, news sites |
| Dynamic Rendering | Serve SSR to bots, CSR to users | ✅ Good— Separate bot experience | Hybrid apps (workaround) |
Decision Tree
Does your content change per-user session?
│
├─► YES → Is it behind authentication?
│ ├─► YES → Client-Side Rendering (CSR) is fine
│ └─► NO → Need SSR or Dynamic Rendering
│
9
└─► NO → How often does content change?
├─► Rarely (docs, guides) → Static Generation (SSG)
├─► Frequently (news, products) → Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
└─► Real-time (stock prices, chat) → Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
React Framework Comparison for SEO
| Feature | Next.js | Remix | Gatsby | Create React App |
| SEO Score | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ (CSR only) |
| Learning Curve | Easy | Medium | Easy | Very Easy |
| SSR Support | ✅ Built-in | ✅ Built-in | ❌ SSG only | ❌ Manual setup |
| SSG Support | ✅ Built-in | ✅ Via adapters | ✅ Built-in | ❌ Need React Snap |
| ISR Support | ✅ Yes | ✅ Via Remix SPA Mode | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Image Optimization | ✅ Automatic | ⚠️ Manual | ✅ gatsby-image | ❌ Manual |
| Meta Tag Management | ✅ next/head | ✅ Built-in | ✅ react-helmet | ⚠️ react-helmet |
| Sitemap Generation | ✅ next-sitemap | ⚠️ Manual | ✅ gatsby-plugin | ❌ Manual |
| Bundle Size (min) | ~70KB | ~50KB | ~50KB | ~40KB |
| Time to First Byte | 50-200ms (ISR) | 100-300ms | 20-50ms | 200-800ms |
| Deployment | Vercel, Netlify | Vercel, Fly.io | Netlify, Gatsby Cloud | Any static host |
| Best For | E-commerce, Blogs | Web apps, Dashboards | Docs, Marketing | Prototypes |
| Community Size | Huge | Growing | Large | Huge |
| React 18 Support | ✅ Full | ✅ Full | ⚠️ Partial | ✅ Full |
| TypeScript | ✅ Native | ✅ Native | ✅ Plugin | ✅ Template |
Recommendation:
- Production site with SEO needs?→ Next.js or Remix
- Content-heavy site (blog, docs)?→ Gatsby or Next.js SSG
- Existing CRA app?→ Migrate to Next.js or add React Snap
- Need bleeding-edge DX?→ Remix

3. Implementing Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
SSR generates HTML on the server for each request, ensuring crawlers receive fully-formed content.
Option 1: Next.js (Recommended)
Next.js is the most popular React SSR framework with built-in SEO optimizations.
Install Next.js:
npx create-next-app@latest my-seo-site
cd my-seo-site
npm run devBasic SSR page:
// pages/products/[id].js
import Head from 'next/head'
export default function Product({ product }) {
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>{product.name} | Your Store</title>
<meta name="description" content={product.description} />
<meta property="og:title" content={product.name} />
<meta property="og:image" content={product.image} />
<link rel="canonical" href={`https://example.com/products/${product.id}`} />
</Head>
<article>
<h1>{product.name}</h1>
<img src={product.image} alt={product.name} width="800" height="600" />
<p>{product.description}</p>
<button>Add to Cart</button>
</article>
</>
)
}
// This runs on the server for each request
export async function getServerSideProps({ params }) {
const res = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/products/${params.id}`)
const product = await res.json()
return {
props: { product }
}
}Why this matters for SEO:Googlebot receives fully-rendered HTML with content, metadata, and structured data—no JavaScript execution required.
Option 2: Remix
Remix is a newer framework with excellent performance characteristics.
// app/routes/products/$id.jsx
import { json } from "@remix-run/node"
import { useLoaderData } from "@remix-run/react"
export async function loader({ params }) {
const product = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/products/${params.id}`)
return json(await product.json())
}
export function meta({ data }) {
return {
title: `${data.name} | Your Store`,
description: data.description,
"og:title": data.name,
"og:image": data.image
}
}
export default function Product() {
const product = useLoaderData()
return (
<article>
<h1>{product.name}</h1>
<img src={product.image} alt={product.name} width="800" height="600" />
<p>{product.description}</p>
</article>
)
}Option 3: Custom SSR with Express
For existing React apps, you can add SSR manually.
// server.js
import express from 'express'
import React from 'react'
import { renderToString } from 'react-dom/server'
import { StaticRouter } from 'react-router-dom/server'
import App from './App'
const app = express()
app.get('*', async (req, res) => {
// Fetch data for this route
const data = await fetchDataForRoute(req.url)
// Render React app to HTML string
const html = renderToString(
<StaticRouter location={req.url}>
<App data={data} />
</StaticRouter>
)
// Send complete HTML document
res.send(`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>${data.title}</title>
<meta name="description" content="${data.description}" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${html}</div>
<script>
window.__INITIAL_DATA__ = ${JSON.stringify(data)}
</script>
<script src="/bundle.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
`)
})
app.listen(3000)Client-side hydration:
// client.js
import React from 'react'
import { hydrateRoot } from 'react-dom/client'
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
import App from './App'
// Reuse server data to avoid refetching
const data = window.__INITIAL_DATA__
hydrateRoot(
document.getElementById('root'),
<BrowserRouter>
<App data={data} />
</BrowserRouter>
)Pro Tip:Always hydrate with the same data used for SSR to avoid content mismatches, which cause React to re-render everything (hurting Core Web Vitals).
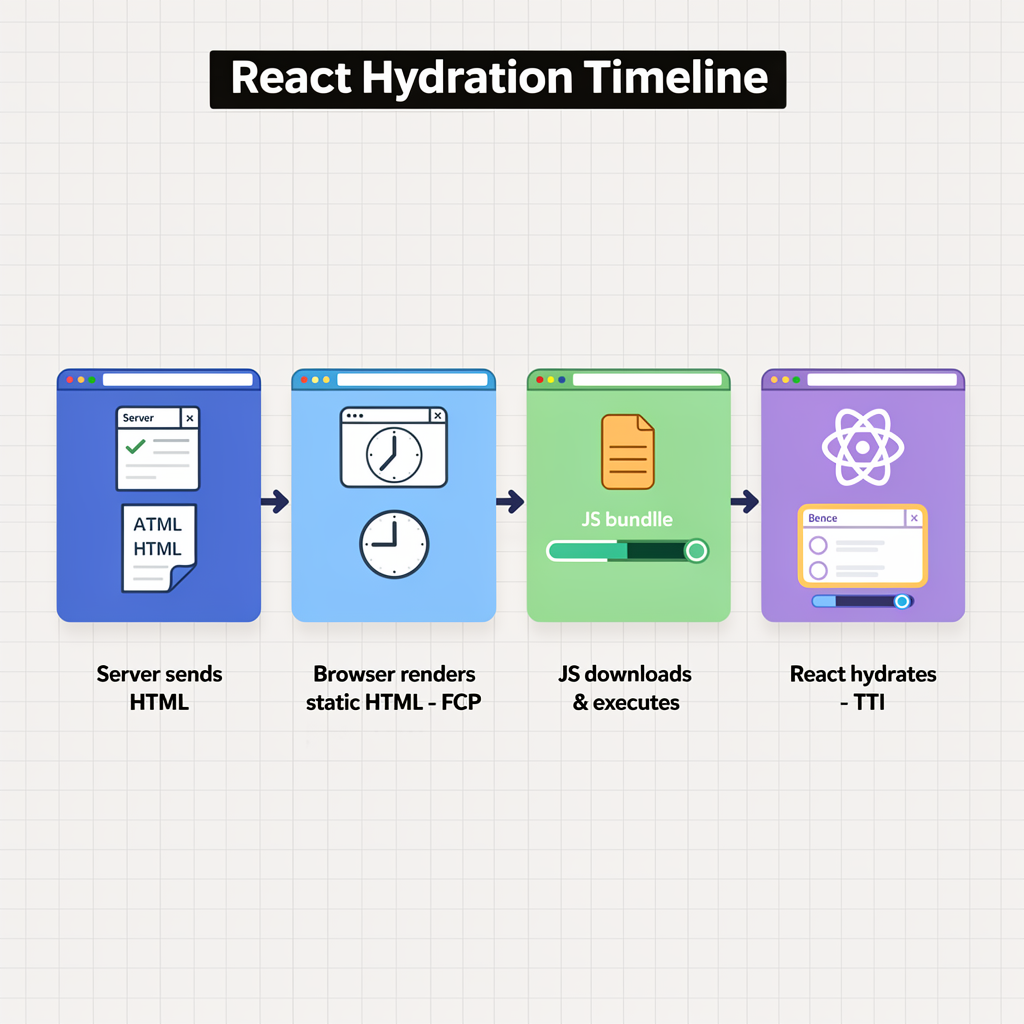
4. Static Site Generation (SSG) & Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
For content that doesn’t change per-request, pre-rendering at build time is the fastest, most SEO-friendly approach.
Static Generation with Next.js
// pages/blog/[slug].js
import Head from 'next/head'
export default function BlogPost({ post }) {
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>{post.title} | Blog</title>
<meta name="description" content={post.excerpt} />
<script type="application/ld+json">
{JSON.stringify({
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BlogPosting",
"headline": post.title,
"datePublished": post.publishedAt,
"author": { "@type": "Person", "name": post.author }
})}
</script>
</Head>
<article>
<h1>{post.title}</h1>
<time dateTime={post.publishedAt}>{post.date}</time>
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: post.content }} />
</article>
</>
)
}
// Generate static paths at build time
export async function getStaticPaths() {
const posts = await fetch('https://api.example.com/posts').then(r => r.json())
return {
paths: posts.map(post => ({ params: { slug: post.slug } })),
fallback: 'blocking' // or false, or true
}
}
// Generate static props at build time
export async function getStaticProps({ params }) {
const post = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/posts/${params.slug}`)
.then(r => r.json())
return {
props: { post },
revalidate: 3600 // ISR: Regenerate every hour
}
}Fallback options:
| Option | Behavior | Use Case |
false | 404 for unpublished pages | Known set of pages |
true | Show loading, fetch data client-side | Large sites, preview mode |
'blocking' | Wait for SSR, then cache | Best SEO, slower first load |
Why this matters for SEO:Static pages load instantly (< 100ms TTFB), have perfect crawlability, and achieve the best Core Web Vitals scores.
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
ISR combines SSG’s speed with SSR’s freshness:
- Serve static page from cache (fast)
- Check if revalidation period expired
- Regenerate in background if needed
- Serve updated page on next request
Perfect for:
- Product catalogs
- News sites
- Content that updates hourly/daily
ISR Performance Benchmarks
| Metric | Traditional SSR | ISR |
| TTFB | 200-800ms | 20-50ms |
| Server CPU | High (every request) | Low (background only) |
| Cache hit rate | N/A | 95-99% |
| Content freshness | Real-time | Delayed by revalidate period |
5. Dynamic Rendering (Fallback Strategy)
Dynamic rendering detects bot traffic and serves pre-rendered HTML, while users get the client-side experience.
⚠️ Google’s stance:Not cloaking if content is equivalent. Use only when SSR/SSG isn’t feasible.
Implementation with Rendertron
// server.js
const express = require('express')
const fetch = require('node-fetch')
const app = express()
const BOT_USER_AGENTS = [
'googlebot',
'bingbot',
'slurp',
'duckduckbot',
'baiduspider',
'yandexbot',
'facebookexternalhit',
'twitterbot',
'linkedinbot'
]
function isBot(userAgent) {
return BOT_USER_AGENTS.some(bot =>
userAgent.toLowerCase().includes(bot)
)
}
app.use(async (req, res, next) => {
const userAgent = req.headers['user-agent'] || ''
if (isBot(userAgent)) {
// Serve pre-rendered HTML to bots
const url = `https://example.com${req.url}`
const rendered = await fetch(`http://rendertron:3000/render/${encodeURIComponent(url)}`)
const html = await rendered.text()
return res.send(html)
}
// Serve normal React app to users
next()
})
app.use(express.static('build'))
app.get('*', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(__dirname + '/build/index.html')
})Prerender.io (Managed Service)
For teams without infrastructure resources, Prerender.io handles bot detection and caching.
// Middleware example
app.use(require('prerender-node')
.set('prerenderToken', 'YOUR_TOKEN')
)Common Dynamic Rendering Mistakes
- Different content for bots— This is cloaking and will get you penalized
- Not caching pre-rendered pages— Defeats the purpose; cache for 24h minimum
- Forgetting social media bots— Facebook, Twitter don’t render JS
- Over-relying on it— Use SSR/SSG when possible; dynamic rendering is a workaround
6. Optimizing React Meta Tags & Structured Data
React Helmet (Framework-Agnostic)
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet-async'
function ProductPage({ product }) {
return (
<>
<Helmet>
<title>{product.name} | Your Store</title>
<meta name="description" content={product.description} />
{/* Open Graph */}
<meta property="og:type" content="product" />
<meta property="og:title" content={product.name} />
<meta property="og:description" content={product.description} />
<meta property="og:image" content={product.image} />
<meta property="og:url" content= {`https://example.com/products/${product.id}`} />
{/* Twitter Card */}
<meta name="twitter:card" content="summary_large_image" />
<meta name="twitter:title" content={product.name} />
<meta name="twitter:description" content={product.description} />
<meta name="twitter:image" content={product.image} />
{/* Canonical */}
<link rel="canonical" href={`https://example.com/products/${product.id}`} />
{/* Structured Data */}
<script type="application/ld+json">
{JSON.stringify({
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": product.name,
"description": product.description,
"image": product.image,
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"price": product.price,
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
}
})}
</script>
</Helmet>
<article>
<h1>{product.name}</h1>
{/* ... */}
</article>
</>
)
}Why this matters for SEO:React Helmet ensures meta tags update when routes change, critical for SPAs where navigation doesn’t reload the page.
Structured Data Best Practices
// utils/structuredData.js
export function generateBreadcrumbSchema(items) {
return {
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "BreadcrumbList",
"itemListElement": items.map((item, index) => ({
"@type": "ListItem",
"position": index + 1,
"name": item.name,
"item": item.url
}))
}
}
export function generateArticleSchema(article) {
return {
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": article.title,
"description": article.excerpt,
"image": article.featuredImage,
"datePublished": article.publishedAt,
"dateModified": article.updatedAt,
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": article.author.name
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Your Company",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://example.com/logo.png"
}
}
}
}
// Usage in component
<Helmet>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{JSON.stringify(generateArticleSchema(article))}
</script>
</Helmet>7. Fixing React Router for SEO
Use HTML5 History API, Not Hash Routing
// ❌ Bad: Hash routing (not crawlable)
import { HashRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
<HashRouter>
<Routes>...</Routes>
</HashRouter>
// URLs look like: example.com/#/products/123
// Google may not index content beyond the #
// ✅ Good: HTML5 history (clean URLs)
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
<BrowserRouter>
<Routes>...</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
// URLs look like: example.com/products/123Server Configuration for Client-Side Routing
When using BrowserRouter, configure your server to always return index.html:
Nginx:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
}Express:
app.use(express.static('build'))
app.get('*', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(__dirname + '/build/index.html')
})Apache (.htaccess):
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.html$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.html [L]
</IfModule>Proper Link Components
// ❌ Bad: onClick navigation (not crawlable)
<div onClick={() => navigate('/products')}>
View Products
</div>
// ✅ Good: Proper <a> tags
import { Link } from 'react-router-dom'
<Link to="/products">
View Products
</Link>
// Renders as <a href="/products">View Products</a>
// Crawlable, accessible, supports right-click/open in new tab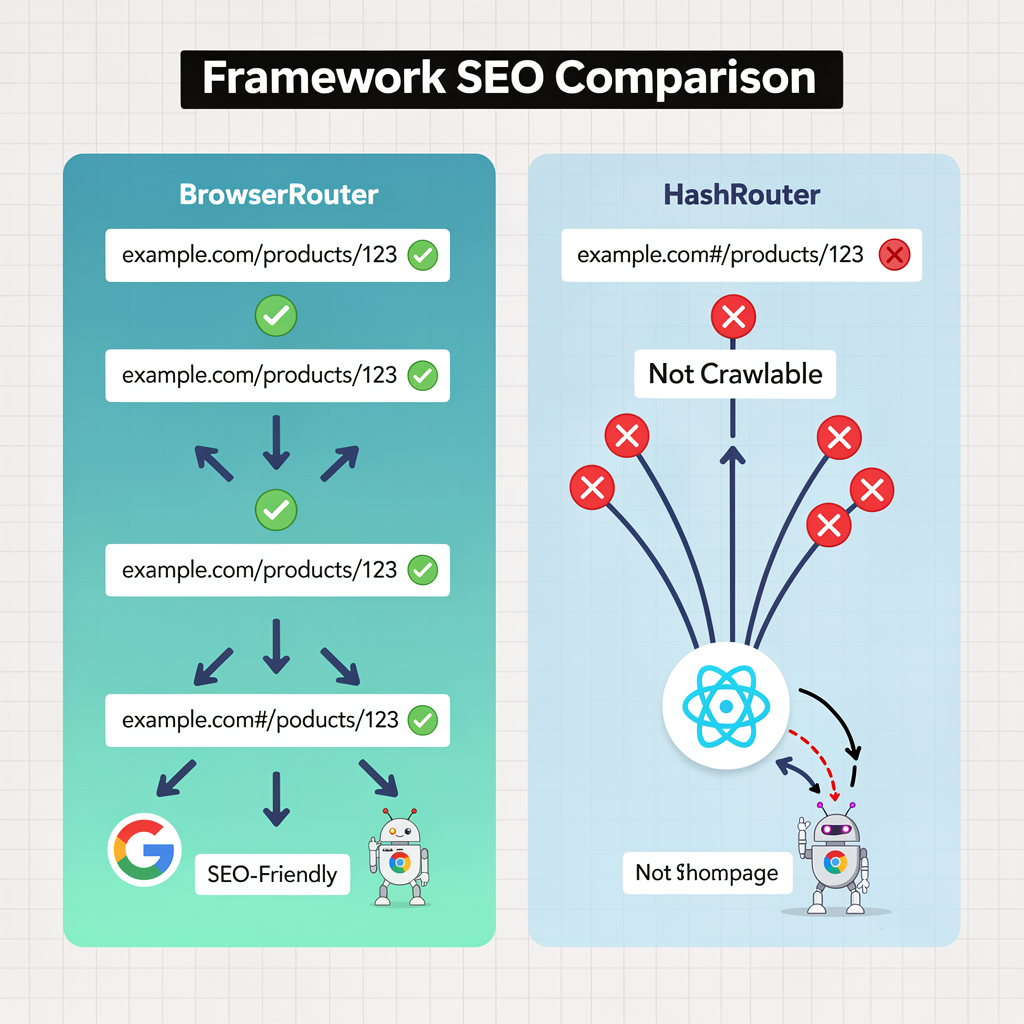
Why this matters for SEO:Clean URLs (BrowserRouter) are fully crawlable and appear as separate pages in search results. Hash URLs (HashRouter) are treated as a single page by search engines, preventing proper indexing of your routes.
Pro Tip:Always use <Link> or <a> for navigation. Googlebot can crawl these. Event-handler navigation is invisible to crawlers.
8. React Performance Optimization for Core Web Vitals
React apps often struggle with Core Web Vitals due to large JavaScript bundles and hydration delays.
Common React CWV Issues
| Issue | Impact | Solution |
| Large JS bundles | High LCP, poor INP | Code splitting, lazy loading |
| Hydration delays | High INP, CLS | Partial hydration, progressive enhancement |
| Unnecessary re-renders | Poor INP | React.memo, useMemo, useCallback |
| Images without dimensions | High CLS | Width/height attributes, aspect-ratio |
| Third-party scripts | All metrics | Defer, async, or remove |
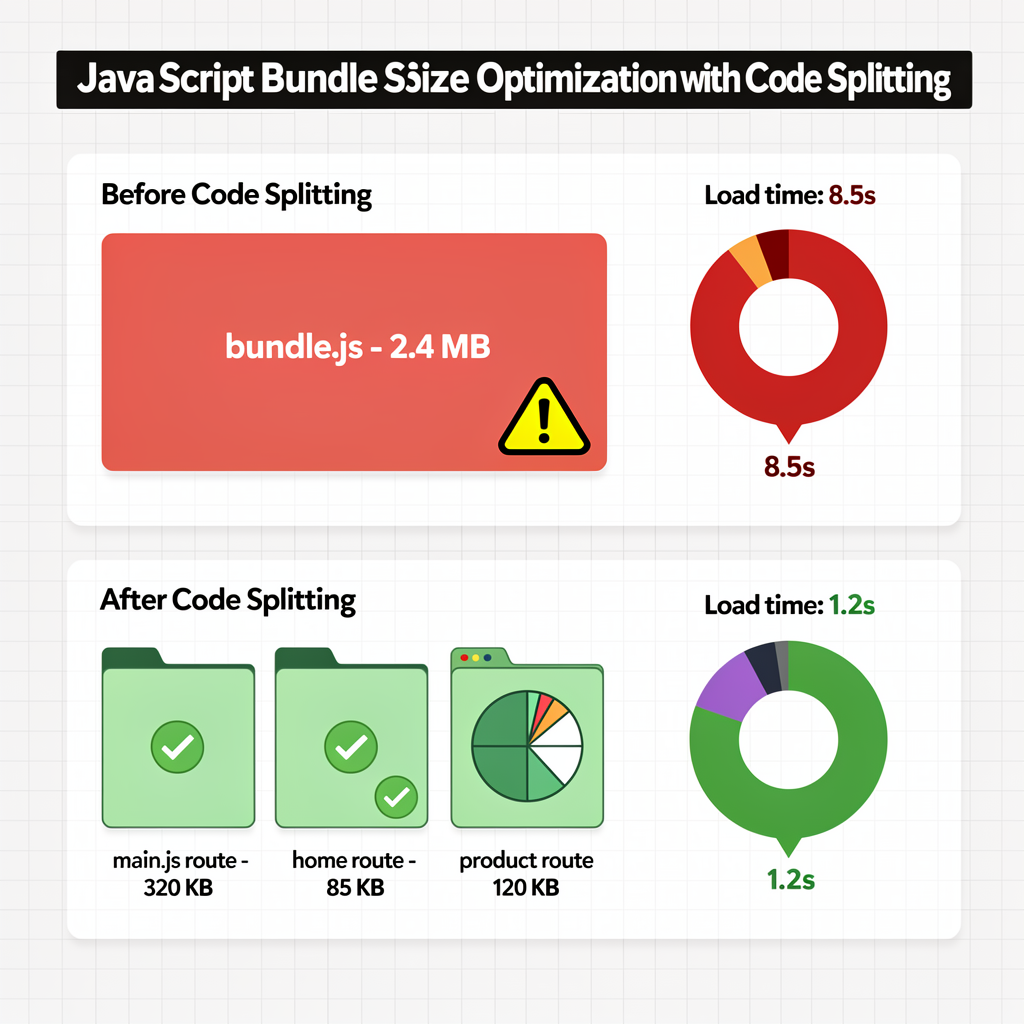
Code Splitting & Lazy Loading
import { lazy, Suspense } from 'react'
// ❌ Before: All components in main bundle
import HeavyChart from './HeavyChart'
import HeavyTable from './HeavyTable'
// ✅ After: Lazy load non-critical components
const HeavyChart = lazy(() => import('./HeavyChart'))
const HeavyTable = lazy(() => import('./HeavyTable'))
function Dashboard() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Dashboard</h1>
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading chart...</div>}>
<HeavyChart />
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading table...</div>}>
<HeavyTable />
</Suspense>
</div>
)
}Route-based code splitting (Next.js does this automatically):
// pages/products/index.js — separate bundle
// pages/blog/index.js — separate bundle
// pages/about.js — separate bundleOptimize Hydration
React hydration is when the client-side JavaScript “takes over” the server-rendered HTML. During hydration, the page is non-interactive.
Strategies to reduce hydration delay:
1. Partial Hydration (Islands Architecture)
Only hydrate interactive components, leave static content as plain HTML.
// With Astro (supports React islands)
---
import Header from '../components/Header.jsx'
import InteractiveCart from '../components/InteractiveCart.jsx'
---
<Header /> <!-- Static, no hydration -->
<InteractiveCart client:load /> <!-- Hydrated -->2. Progressive Hydration
Hydrate components as they become visible.
// Custom progressive hydration hook
import { useEffect, useState, useRef } from 'react'
function useProgressiveHydration() {
const ref = useRef()
const [isHydrated, setIsHydrated] = useState(false)
useEffect(() => {
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(([entry]) => {
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
setIsHydrated(true)
observer.disconnect()
}
})
if (ref.current) observer.observe(ref.current)
return () => observer.disconnect()
}, [])
return [ref, isHydrated]
}
// Usage
function HeavyComponent() {
const [ref, isHydrated] = useProgressiveHydration()
if (!isHydrated) {
return <div ref={ref}>Loading...</div>
}
return <ExpensiveInteractiveComponent />
}3. Streaming SSR (React 18+)
Send HTML as it’s generated, hydrate progressively.
// Next.js 13+ with app directory (Suspense streaming)
import { Suspense } from 'react'
export default function Page() {
return (
<>
<Header /> {/* Renders immediately */}
<Suspense fallback={<Skeleton />}>
<SlowComponent /> {/* Streams when ready */}
</Suspense>
</>
)
}Prevent Unnecessary Re-renders
// ❌ Before: Child re-renders on every parent update
function Parent() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const expensiveValue = computeExpensiveValue()
const handleClick = () => doSomething()
return <Child value={expensiveValue} onClick={handleClick} />
}
// ✅ After: Memoize expensive computations and callbacks
import { useMemo, useCallback } from 'react'
function Parent() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const expensiveValue = useMemo(() => computeExpensiveValue(), [])
const handleClick = useCallback(() => doSomething(), [])
return <Child value={expensiveValue} onClick={handleClick} />
}
// ✅ Memoize the child component itself
const Child = React.memo(({ value, onClick }) => {
return <button onClick={onClick}>{value}</button>
})Image Optimization
// Next.js Image component (automatic optimization)
import Image from 'next/image'
<Image
src="/hero.jpg"
alt="Hero image"
width={1200}
height={630}
priority // Preload LCP image
sizes="(max-width: 768px) 100vw, 50vw"
/>For more on image optimization and Core Web Vitals, see Advanced Core Web Vitals.

9. Handling Authentication & Personalization
SEO for Authenticated Pages
Content behind login should use CSR (no SEO needed), but login/signup pages themselves need SSR.
// pages/login.js
export default function Login() {
const [email, setEmail] = useState('')
const [password, setPassword] = useState('')
return (
<>
<Head>
<title>Login | Your App</title>
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow" />
</Head>
<form onSubmit={handleLogin}>
<input type="email" value={email} onChange={e => setEmail(e.target.value)} />
<input type="password" value={password} onChange={e => setPassword(e.target.value)} />
<button type="submit">Login</button>
</form>
</>
)
}
// No getServerSideProps needed—static page with noindexPersonalized Content
For pages with personalization, use a hybrid approach:
export default function ProductPage({ product, recommendations }) {
// Server-rendered product data (SEO-critical)
// Client-rendered recommendations (personalized)
const [personalizedRecs, setPersonalizedRecs] = useState(recommendations)
useEffect(() => {
// Fetch personalized recommendations client-side
fetchPersonalizedRecs().then(setPersonalizedRecs)
}, [])
return (
<>
{/* SEO-critical content (SSR) */}
<article>
<h1>{product.name}</h1>
<p>{product.description}</p>
</article>
{/* Personalized content (CSR) */}
<section>
<h2>Recommended for You</h2>
{personalizedRecs.map(rec => <ProductCard key={rec.id} {...rec} />)}
</section>
</>
)
}
export async function getServerSideProps({ params }) {
const product = await fetchProduct(params.id)
const recommendations = await fetchDefaultRecommendations(params.id)
return { props: { product, recommendations } }
}10. Testing & Validation
Tools for React SEO Audits
1. Google Search Console
- Check “Coverage” report for indexing issues
- Monitor “Core Web Vitals” for performance
- Use “URL Inspection” tool to see rendered HTML
2. Mobile-Friendly Test
- https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly
- Shows how Googlebot renders your React app
3. Rich Results Test
- https://search.google.com/test/rich-results
- Validates structured data
4. Lighthouse
npx lighthouse https://example.com –view
5. React DevTools Profiler
- Identifies slow components
- Measures render times
Manual Testing Checklist
- View source (Ctrl+U) shows content, not empty
<div id="root"> - Meta tags update on route change
- Internal links use
<a href>, notonClick - Images have width/height attributes
- Structured data validates in Rich Results Test
- No console errors or React warnings
- Fast First Contentful Paint (< 1.8s)
- Low Cumulative Layout Shift (< 0.1)
Automated Testing
// tests/seo.test.js (using Puppeteer)
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer')
describe('SEO tests', () => {
let browser, page
beforeAll(async () => {
browser = await puppeteer.launch()
page = await browser.newPage()
})
afterAll(async () => {
await browser.close()
})
test('page has correct title', async () => {
await page.goto('https://example.com/products/123')
const title = await page.title()
expect(title).toBe('Product Name | Your Store')
})
test('page has meta description', async () => {
await page.goto('https://example.com/products/123')
const description = await page.$eval(
'meta[name="description"]',
el => el.content
)
expect(description).toBeTruthy()
})
test('page has structured data', async () => {
await page.goto('https://example.com/products/123')
const schema = await page.$eval(
'script[type="application/ld+json"]',
el => JSON.parse(el.textContent)
)
expect(schema['@type']).toBe('Product')
})
test('internal links are crawlable', async () => {
await page.goto('https://example.com')
const links = await page.$$eval('a[href]', anchors =>
anchors.map(a => a.href)
)
expect(links.length).toBeGreaterThan(0)
expect(links.every(link => !link.includes('#/'))).toBe(true)
})
})11. Essential Tools & Plugins for React SEO
The right tools can streamline React SEO implementation and catch issues before they reach production.
React-Specific SEO Libraries
1. React Helmet Async
The most popular solution for managing <head> tags in React.
npm install react-helmet-async
// Wrap your app with HelmetProvider
import { HelmetProvider } from 'react-helmet-async'
function App() {
return (
<HelmetProvider>
<YourRoutes />
</HelmetProvider>
)
}
// Use in any component
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet-async'
function ProductPage({ product }) {
return (
<>
<Helmet>
<title>{product.name} | Store</title>
<meta name="description" content={product.description} />
<link rel="canonical" href={`https://example.com/products/${product.id}`} />
{/* Dynamic Schema */}
<script type="application/ld+json">
{JSON.stringify({
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": product.name,
"offers": { "@type": "Offer", "price": product.price }
})}
</script>
</Helmet>
<article>{/* ... */}</article>
</>
)
}Why this matters for SEO:React Helmet ensures meta tags update on every route change, critical for SPAs where navigation doesn’t reload the page.
2. Next SEO
Simplified SEO management for Next.js projects.
npm install next-seo
import { NextSeo, ArticleJsonLd } from 'next-seo'
function BlogPost({ post }) {
return (
<>
<NextSeo
title={post.title}
description={post.excerpt}
canonical={`https://example.com/blog/${post.slug}`}
openGraph={{
type: 'article',
article: {
publishedTime: post.publishedAt,
authors: [post.author.name]
},
images: [{ url: post.featuredImage }]
}}
/>
<ArticleJsonLd
url={`https://example.com/blog/${post.slug}`}
title={post.title}
images={[post.featuredImage]}
datePublished={post.publishedAt}
authorName={post.author.name}
description={post.excerpt}
/>
<article>{/* ... */}</article>
</>
)
}3. React Snap (Pre-rendering)
Pre-render Create React App pages to static HTML.
npm install react-snap
// package.json
{
"scripts": {
"postbuild": "react-snap"
},
"reactSnap": {
"inlineCss": true,
"minifyHtml": true
}
}Runs after npm run build to generate static HTML for all routes.
SEO Analysis Tools
1. Screaming Frog SEO Spider (JavaScript Rendering)
- Crawl React apps with JS rendering enabled
- Compare “HTML” vs “Rendered” views
- Identify missing content, broken links, duplicate titles
Configuration for SPAs:
- Enable JavaScript rendering in Configuration → Spider
- Set “Render mode” to “JavaScript”
- Increase “Max render time” for slow-loading apps
2. Google Lighthouse CI
Automate Lighthouse audits in CI/CD.
# .github/workflows/lighthouse.yml
name: Lighthouse CI
on: [push]
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v10
with:
urls: |
https://staging.example.com
https://staging.example.com/products/featured
budgetPath: ./lighthouse-budget.json3. Vercel Analytics / Web Vitals
Real-user monitoring built into Vercel deployments.
// pages/_app.js (Next.js)
import { Analytics } from '@vercel/analytics/react'
export default function App({ Component, pageProps }) {
return (
<>
<Component {...pageProps} />
<Analytics />
</>
)
}Tracks Core Web Vitals automatically, segmented by page and device.
Debugging & Monitoring Tools
1. Chrome DevTools Coverage Tab
Identify unused JavaScript in your React bundles.
- Open DevTools → Coverage tab
- Record page load
- See % of unused code per file
- Code-split or lazy-load unused routes
2. React DevTools Profiler
Find slow component renders affecting INP.
- Install React DevTools extension
- Open Profiler tab
- Record interactions
- Identify components with long render times
3. Bundle Analyzer
# Next.js
npm install @next/bundle-analyzer
// next.config.js
const withBundleAnalyzer = require('@next/bundle-analyzer')({
enabled: process.env.ANALYZE === 'true'
})
module.exports = withBundleAnalyzer({})
Run ANALYZE=true npm run build to visualize bundle size.Sitemap Generation
Dynamic Sitemap for Next.js:
// pages/sitemap.xml.js
export async function getServerSideProps({ res }) {
const baseUrl = 'https://example.com'
const pages = await fetchAllPages()
const sitemap = `<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
${pages.map(page => `
<url>
<loc>${baseUrl}${page.url}</loc>
<lastmod>${page.updatedAt}</lastmod>
<priority>${page.priority}</priority>
</url>
`).join('')}
</urlset>`
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/xml')
res.write(sitemap)
res.end()
return { props: {} }
}
export default function Sitemap() {}Pro Tip:Use next-sitemap package for automatic sitemap generation in Next.js with zero configuration.
Schema Validation Tools
1. Google Rich Results Test
- https://search.google.com/test/rich-results
- Paste URL or code snippet
- Validates Product, Article, FAQ, Breadcrumb schemas
2. Schema.org Validator
- https://validator.schema.org/
- More lenient than Google’s tool
- Useful for debugging JSON-LD syntax
3. Structured Data Linter
- http://linter.structured-data.org/
- Validates and visualizes structured data
12. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and React SEO
React PWAs introduce unique SEO challenges around service workers, app shells, and offline content.
Service Workers and Crawlability
Challenge:Service workers can intercept requests, potentially serving stale content to Googlebot.
Solution:Differentiate bot traffic in your service worker.
// service-worker.js
self.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
const userAgent = event.request.headers.get('user-agent') || ''
const isBot = /googlebot|bingbot|slurp/i.test(userAgent)
if (isBot) {
// Always fetch fresh content for bots
event.respondWith(fetch(event.request))
} else {
// Cache-first strategy for users
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request)
.then(response => response || fetch(event.request))
)
}
})Why this matters for SEO:Ensures Googlebot always sees fresh, server-rendered content while users benefit from cached performance.
App Shell Architecture
The app shell (navigation, header, footer) loads instantly, but content loads dynamically.
SEO Risk:Empty content area before JS executes.
Solution:SSR the initial content, not just the shell.
// Next.js handles this automatically
export async function getServerSideProps() {
const content = await fetchContent()
return { props: { content } }
}
export default function Page({ content }) {
return (
<>
<AppShell /> {/* Navigation, header, footer */}
<main>{content}</main> {/* Server-rendered */}
</>
)
}Manifest.json and SEO
While manifest.json isn’t a ranking factor, it affects discoverability.
// public/manifest.json
{
"name": "Your App Name",
"short_name": "App",
"description": "SEO-friendly description of your app",
"start_url": "/",
"display": "standalone",
"theme_color": "#000000",
"background_color": "#ffffff",
"icons": [
{
"src": "/icon-192.png",
"sizes": "192x192",
"type": "image/png",
"purpose": "any maskable"
},
{
"src": "/icon-512.png",
"sizes": "512x512",
"type": "image/png"
}
]
}Link in HTML:
<link rel="manifest" href="/manifest.json">Offline Content and Indexing
Question:Does cached offline content get indexed?
Answer:No. Googlebot doesn’t use service worker caches. Only the online, server-rendered version matters.
Best practice:Use SSR/SSG for all public pages, then add PWA features on top for user experience.
PWA SEO Checklist
- Service worker doesn’t block Googlebot from fetching fresh content
- App shell doesn’t hide main content from crawlers
- Manifest.json includes descriptive name and description
- All public routes have SSR/SSG versions
- Offline page has helpful messaging (not indexed, but UX matters)
- Meta tags update on client-side navigation
- No splash screens blocking content on first load
For more on PWA performance optimization, see How to Make Your Website Faster.
13. Framework-Specific SEO Guides
Next.js SEO Best Practices
// next.config.js
module.exports = {
// Generate sitemap automatically
async rewrites() {
return [
{
source: '/sitemap.xml',
destination: '/api/sitemap'
}
]
},
// Enable image optimization
images: {
domains: ['cdn.example.com'],
formats: ['image/avif', 'image/webp']
},
// Configure headers for security/SEO
async headers() {
return [
{
source: '/:path*',
headers: [
{
key: 'X-DNS-Prefetch-Control',
value: 'on'
},
{
key: 'X-Frame-Options',
value: 'SAMEORIGIN'
}
]
}
]
}
}Sitemap generation:
// pages/api/sitemap.js
export default async function handler(req, res) {
const posts = await fetchAllPosts()
const products = await fetchAllProducts()
const sitemap = `<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://example.com</loc>
<lastmod>${new Date().toISOString()}</lastmod>
<priority>1.0</priority>
</url>
${posts.map(post => `
<url>
<loc>https://example.com/blog/${post.slug}</loc>
<lastmod>${post.updatedAt}</lastmod>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
`).join('')}
${products.map(product => `
<url>
<loc>https://example.com/products/${product.id}</loc>
<lastmod>${product.updatedAt}</lastmod>
<priority>0.7</priority>
</url>
`).join('')}
</urlset>`
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/xml')
res.write(sitemap)
res.end()
}Remix SEO Best Practices
// root.jsx
import { Links, LiveReload, Meta, Outlet, Scripts, ScrollRestoration } from "@remix-run/react"
export function meta() {
return {
charset: "utf-8",
viewport: "width=device-width,initial-scale=1",
}
}
export function links() {
return [
{ rel: "preconnect", href: "https://fonts.googleapis.com" },
{ rel: "preconnect", href: "https://fonts.gstatic.com", crossOrigin: "anonymous" },
{ rel: "stylesheet", href: "https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Inter:wght@400;700&display=swap" }
]
}
export default function App() {
return (
<html lang="en">
<head>
<Meta />
<Links />
</head>
<body>
<Outlet />
<ScrollRestoration />
<Scripts />
<LiveReload />
</body>
</html>
)
}Gatsby SEO Best Practices
Gatsby uses SSG by default—excellent for SEO.
// gatsby-config.js
module.exports = {
plugins: [
'gatsby-plugin-react-helmet',
'gatsby-plugin-sitemap',
{
resolve: 'gatsby-plugin-robots-txt',
options: {
policy: [{ userAgent: '*', allow: '/' }]
}
},
{
resolve: 'gatsby-plugin-manifest',
options: {
name: 'Your Site',
short_name: 'Site',
start_url: '/',
icon: 'src/images/icon.png'
}
}
]
}14. Common React SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Critical Mistakes That Kill Rankings
1. Empty Initial HTML
Problem:View source shows <div id="root"></div> with no content.
Solution:Use SSR, SSG, or pre-rendering. Verify by viewing source (not DevTools).
2. Hash Routing
Problem:URLs like example.com/#/products/123 aren’t crawled properly.
Solution:Use BrowserRouter with HTML5 history API.
3. Missing Meta Tags
Problem:Title/description don’t update on route change.
Solution:Use React Helmet or framework-native solutions.
4. JavaScript-Only Links
Problem:Navigation via onClick handlers.
Solution:Always use <Link> or <a href> tags.
5. Lazy Loading Above-the-Fold
Problem:Hero images/content lazy-loaded, harming LCP.
Solution:Eager-load critical content, lazy-load below-the-fold only.
6. Large JavaScript Bundles
Problem:2MB+ bundles delay Time to Interactive.
Solution:Code-split by route, lazy-load components, tree-shake dependencies.
7. No Structured Data
Problem:Missing out on rich results, knowledge panels.
Solution:Add JSON-LD for articles, products, FAQs, breadcrumbs.
8. Forgetting robots.txt & Sitemap
Problem:Googlebot can’t discover all pages efficiently.
Solution:Generate dynamic sitemap, submit to Search Console.
15. Prioritizing React SEO Fixes by Impact
Not all issues are equally important. Use this matrix:
| Issue | SEO Impact | Dev Effort | Priority |
| Empty initial HTML (CSR) | Critical | High | P0 |
| Missing SSR for key pages | Critical | High | P0 |
| Hash routing | Critical | Low | P0 |
| Large JS bundles (> 1MB) | High | Medium | P1 |
| Missing meta tags | High | Low | P1 |
| No structured data | Medium | Low | P2 |
| Slow hydration | Medium | High | P2 |
| Missing sitemap | Low | Low | P3 |
Framework migration ROI:
| Current Stack | Recommended Upgrade | Expected Traffic Lift | Effort |
| Create React App (CSR) | Next.js (SSR/SSG) | +40-60% | 2-4 weeks |
| Custom CSR setup | Remix (SSR) | +40-60% | 2-4 weeks |
| Hash routing SPA | HTML5 history + SSR | +30-50% | 1-2 weeks |
| CRA + Prerender.io | Next.js SSG | +20-40% | 1-3 weeks |
16. Case Study: E-commerce Migration to Next.js
Scenario:Fashion e-commerce site with 10,000 products, previously built with Create React App (CSR).
Before (CSR)
- Indexation:40% of products indexed (4,000/10,000)
- Avg. TTFB:200ms
- Avg. LCP:4.2s (Poor)
- Organic traffic:50,000/month
- Revenue from organic:$200,000/month
After (Next.js ISR)
- Indexation:95% of products indexed (9,500/10,000)
- Avg. TTFB:50ms (ISR cache hit)
- Avg. LCP:1.8s (Good)
- Organic traffic:85,000/month (+70%)
- Revenue from organic:$350,000/month (+75%)
Key Changes
- Static generation for category pages— Build-time rendering for
/category/* - ISR for product pages—
revalidate: 3600(hourly updates) - Structured data— Product schema for rich results
- Image optimization— Next.js Image component with WebP
- Code splitting— Reduced main bundle from 1.8MB to 320KB
Total dev time:6 weeks with 2 engineers.
ROI:$150k additional monthly revenue → $1.8M annually.
Conclusion
React SEO isn’t inherently broken—but default client-side rendering creates significant obstacles. The solution is choosing the right rendering strategy for each page type:
- SSGfor static pages (docs, landing pages)
- ISRfor semi-static content (products, articles)
- SSRfor dynamic, personalized content
- CSRonly for authenticated, user-specific interfaces
Modern frameworks like Next.js and Remix make this straightforward, with built-in SEO optimizations and performance best practices.
Action Plan
- Audit your current setup— View source; if empty, you need SSR/SSG
- Choose a framework— Next.js (most popular), Remix (best DX), or Gatsby (SSG-only)
- Migrate high-value pages first— Homepage, top products, key landing pages
- Measure impact— Track indexation, rankings, Core Web Vitals
- Expand gradually— Migrate remaining pages once proven
For professional React SEO implementation, explore LinkGraph’s Technical SEO Services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Google crawl my React app without SSR?
Yes, but with major limitations. Googlebot can render JavaScript, but JS-rendered content enters a secondary indexing queue, may take days/weeks to index, and can fail entirely due to timeouts or errors. For competitive keywords, SSR is essential.
What’s the fastest way to add SEO to an existing React app?
Quick wins (1-3 days):
- Add React Helmet for dynamic meta tags
- Switch from HashRouter to BrowserRouter
- Add structured data (JSON-LD)
Medium-term (1-2 weeks):4. Implement pre-rendering with Prerender.io or Rendertron 5. Add a sitemap
Long-term (2-4 weeks):6. Migrate to Next.js for proper SSR/SSG
Is Next.js the only option for React SEO?
No, but it’s the most popular. Alternatives:
- Remix— Modern, excellent DX, built-in performance optimizations
- Gatsby— SSG-only, great for content sites
- Custom SSR— Full control, but requires more setup
- Astro— Partial hydration, framework-agnostic
How do I handle SEO for single-page apps (SPAs)?
SPAs need special attention:
- Use HTML5 history routing (no hashes)
- Update
<title>and meta tags on route change - Use SSR or pre-rendering for public pages
- Ensure internal links use
<a>tags - Generate a dynamic sitemap
Does React hurt Core Web Vitals?
It can, but doesn’t have to:
- LCP— Large bundles delay rendering; code-split and SSR
- CLS— Hydration can cause layout shifts; match SSR HTML exactly
- INP— Heavy re-renders block interactions; memoize and optimize
See Advanced Core Web Vitalsfor React-specific optimizations.
Can I use React for a blog and still rank well?
Yes, with SSG/SSR:
- Next.js:
getStaticPropsfor blog posts - Gatsby:Built for content sites
- Remix:Excellent for dynamic blogs
Avoid CSR for blogs—content must be in initial HTML.
React SEO Checklist PDF
Download our comprehensive React SEO checklistto ensure you don’t miss any critical optimization.
What’s Included:
✅ Pre-Launch Checklist(15 items)
- SSR/SSG verification
- Meta tags audit
- Structured data validation
- Router configuration
- Sitemap submission
✅ Performance Checklist(12 items)
- Code splitting verification
- Bundle size optimization
- Image optimization
- Core Web Vitals targets
- Lighthouse score thresholds
✅ Framework-Specific Checklists
- Next.js optimization (10 items)
- Remix best practices (8 items)
- Gatsby configuration (7 items)
- CRA migration path (5 steps)
✅ Monitoring Checklist(8 items)
- GSC setup
- Analytics configuration
- Error tracking
- Performance monitoring
Download Options:
Option 1: Interactive Playground
Use our interactive SSR vs CSR demoto visualize rendering differences
Option 2: View Below
Complete checklist with checkboxes ⬇️
Complete React SEO Checklist
1. Pre-Launch Checklist
Rendering Strategy
- Verified SSR/SSG is working (view source shows content)
- No hash routing (#/) in URLs
- All public pages have server-rendered HTML
- Dynamic routes are pre-rendered or SSR-enabled
Meta Tags & Structured Data
- Every page has unique
<title>tag - Every page has unique meta description
- Canonical URLs set correctly
- Open Graph tags for social sharing
- Twitter Card tags configured
- JSON-LD structured data implemented
- Schema.org validation passed
Technical Configuration
- robots.txt allows crawling of public pages
- XML sitemap generated and submitted to GSC
- 404 page returns 404 status code (not 200)
- Redirects use 301 (permanent) not 302
- Internal links use
<a href>, not onClick handlers - Images have width/height attributes
- Alt text on all images
2. Performance Checklist
Code Optimization
- Route-based code splitting enabled
- Main bundle < 200 KB gzipped
- Lazy loading for below-fold components
- Tree-shaking configured properly
- Removed unused dependencies
Core Web Vitals
- LCP < 2.5s (75th percentile)
- CLS < 0.1
- INP < 200ms
- FCP < 1.8s
- TTFB < 800ms
Image & Asset Optimization
- Images converted to WebP/AVIF
- Responsive images with srcset
- LCP image has fetchpriority=”high”
- Critical CSS inlined
- Fonts preloaded
- Third-party scripts deferred
3. Next.js Specific
- Using next/image for all images
- getStaticProps for static pages
- getServerSideProps for dynamic pages
- ISR with revalidate for semi-static content
- next-sitemap configured
- next-seo or custom Head component
- Custom _document.js for global meta tags
- Lighthouse CI in deployment pipeline
- Vercel Analytics or similar RUM tool
- Environment variables properly configured
4. Remix Specific
- Loader functions return proper meta
- Links component used for navigation
- ErrorBoundary on all routes
- Proper cache headers configured
- Sitemap route implemented
- Meta function exports on all routes
- Optimistic UI doesn’t break SEO
- Server-side session handling
5. Gatsby Specific
- gatsby-plugin-react-helmet installed
- gatsby-plugin-sitemap configured
- gatsby-plugin-robots-txt added
- Image optimization with gatsby-image
- SEO component created and reused
- Build time < 5 minutes (for CI/CD)
- Incremental builds enabled (Gatsby Cloud)
6. Monitoring & Maintenance
- Google Search Console verified
- Google Analytics 4 configured
- Core Web Vitals monitoring active
- Error tracking (Sentry, Bugsnag)
- Performance monitoring (SpeedCurve, Calibre)
- Weekly GSC indexing report review
- Monthly Lighthouse audit
- Quarterly competitor analysis
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Not using React Helmet or framework equivalent
- Lazy-loading above-the-fold content
- Using hash routing (#/) for public pages
- Missing canonical URLs
- No sitemap or outdated sitemap
- Blocking Googlebot in robots.txt
- Not testing in Google Rich Results Test
- Forgetting social meta tags
Interactive Playground
Try our live SSR vs CSR comparison toolto see how search engines view your React application.
Interactive Demo Features:
✅ Side-by-side comparison– View SSR and CSR HTML simultaneously
✅ Real HTML source visualization– See exactly what Googlebot sees
✅ Performance metrics– TTFB, FCP, LCP, and indexability scores
✅ Copy-to-clipboard– Grab code examples instantly
✅ Mobile responsive– Test on any device
Access the Playground:
Option 1: Embedded Version(WordPress/Blog)
<iframe
src="https://linkgraph.com/tools/react-seo-playground.html"
width="100%"
height="700px"
frameborder="0"
title="React SEO Interactive Playground"
loading="lazy">
</iframe>Option 2: Standalone Version
Open Full-Screen Playground
Bookmark this for quick reference during development
What You’ll Learn:
- Initial HTML Comparison– See empty
<div id="root"></div>(CSR) vs. full content (SSR) - Meta Tag Visibility– Understand why SSR meta tags work better for social sharing
- Performance Impact– Compare LCP times and Time to Interactive
- Indexability Scores– Visualize why SSR gets 100% indexation vs. CSR’s ~60%
- Real Code Examples– Copy production-ready HTML from both approaches
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Can Google crawl my React app without SSR?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Yes, but with major limitations. Googlebot can render JavaScript, but JS-rendered content enters a secondary indexing queue, may take days/weeks to index, and can fail due to timeouts. For competitive keywords, SSR is essential."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What's the fastest way to add SEO to an existing React app?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Quick wins: Add React Helmet for meta tags, switch to BrowserRouter, add structured data. Medium-term: Implement pre-rendering. Long-term: Migrate to Next.js for SSR/SSG."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Is Next.js the only option for React SEO?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "No. Alternatives include Remix (modern, excellent DX), Gatsby (SSG-only), custom SSR (full control), and Astro (partial hydration). Next.js is just the most popular."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Does React hurt Core Web Vitals?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "It can. Large bundles delay LCP, hydration causes CLS, and heavy re-renders hurt INP. Solutions: code-split, SSR for critical content, memoize components, and optimize images."
}
}
]
}
</script>Further Reading
Core Web Vitals & Performance
- What Are Core Web Vitals? Complete Introduction
- Advanced Core Web Vitals: Diagnose & Fix Guide
- How to Make Your Website Faster
- Page Speed Optimization Services
Technical SEO & Auditing
- Technical SEO Audit Checklist
JavaScript & Structured Data
- Structured Data for SEO: Complete Guide
