How to Achieve Optimal On-Page SEO – The 10 Definitive Factors
Search engine optimization is a multi-faceted behemoth, encompassing the on-site, off-site, technical, analytical, content, and whole-site optimization efforts that allow your page or site to be easily […]
Search engine optimization is a multi-faceted behemoth, encompassing the on-site, off-site, technical, analytical, content, and whole-site optimization efforts that allow your page or site to be easily found and highly ranked in search results. However, every different type of SEO is intertwined with the others, so it’s important to understand–and master–all of them. But don’t worry–it’s totally doable! We’re here to help you tame the SEO beast step-by-step. Today, in this complete guide to onpage SEO we’re tackling on-page optimizations and their impact on your rankings. Onpage optimization in SEO is one of the factors we actually have full control over, so play to win!
To understand on-page SEO, we must first define it. Specifically, on-page SEO refers to both the visible content your readers see on your page within their browser window as well as the invisible content read by the search engine bots (also known as Googlebot, Bingbot, Facebook Bot, etc.). This invisible content includes the HTML markup that your browser and bots interpet, like meta tags, your title tag, heading tags (H1s and H2s), structured data markup schema (courtesy of schema.org), rich snippets, and a few other types that we’ll explore.
So, SEO warriors, if you’re ready, let’s dig a little deeper into the particulars of everything on-page SEO Get ready to not only build your SEO vocabulary, but learn what you’ve applied so your product or service shows up at the top of the SERPs and you get lots of healthy organic traffic!
1. Content Quality and Keyword Research
Why should Google put your page ahead of your competitors in search results? No seriously. Think about it. What’s unique that your site brings to the table?
After working with literally hundreds of different digital brands, we’ve seen repeatedly the impact of keyword research and high quality content. Thoroughly researching keywords with high search volume, low relative difficulty, and semantic relevance to your site’s existing content are vital to getting pages to rank well. Thin content, duplicate content, keyword stuffing: this stuff doesn’t work anymore, and there are no shortcuts! Spend the time to hire a quality writer, hire us, or write well researched long-form content yourself. We have advanced proprietary tools to perform content audits and help get your content optimized; our crawlers spider Google’s first page results and pinpoint keyword phrases that Google deems relevant for your targeted keyword. We use this keyword phrase and keyword density data after we draft high quality pieces to imbue them with any relevant topics we may have forgotten to cover.
As far as onpage ranking factors go, this one is easily the most important. Want to rank for “personal injury lawyer Chicago”? That keyword better be in your content somewhere, and you better have related keyword phrases like “car accidents”, “motorcycle accidents”, “motor vehicle accidents”, “workers compensation”, “lost wages”, “insurance company”, and “medical bills”. That’s how this works.
Adding rich media and graphic content like images, embedded youtube/vimeo videos, and embedded tweets also increases the value of your page content. Also make use of bulleted or numbered lists where appropriate. Just don’t drop a blob of content on the page. You can use the onpage audit tool in your dashboard to identify where your content signals need the most attention.
2. Responsive Design
What does your site look like on your mobile phone, tablet, and different desktop screen sizes? No one likes to go to a site on their phone only to find that you can’t see a full image on a page without manipulating horizontal and vertical scroll bars. The pro move here is to make sure your site has the right CSS code for each of the common device types. Any front-end developer worth their salt can do this in their sleep with their left hand, but just in case you’re short one sleepy right-handed developer, here’s a list of media queries for these different screen resolutions. If you’re on a custom site, especially one that was designed more than five years ago, you’ll most likely need to use these queries to revamp your front-end design.
If you built your site using a front-end framework like Bootstrap or Foundation, or if you’re using a WordPress theme built on one of these front-end frameworks (most of the good ones are), you’ll probably have pretty good responsiveness out of the box.
We’ve used Bootstrap and Foundation and recommend them both.
So, does this page pass the responsiveness test? Click here and use our nifty responsiveness tool to check it out! We’ll give you a second….
Yep! We’re looking good! Now might be a good time to test your page if you haven’t already.
3. Content Length
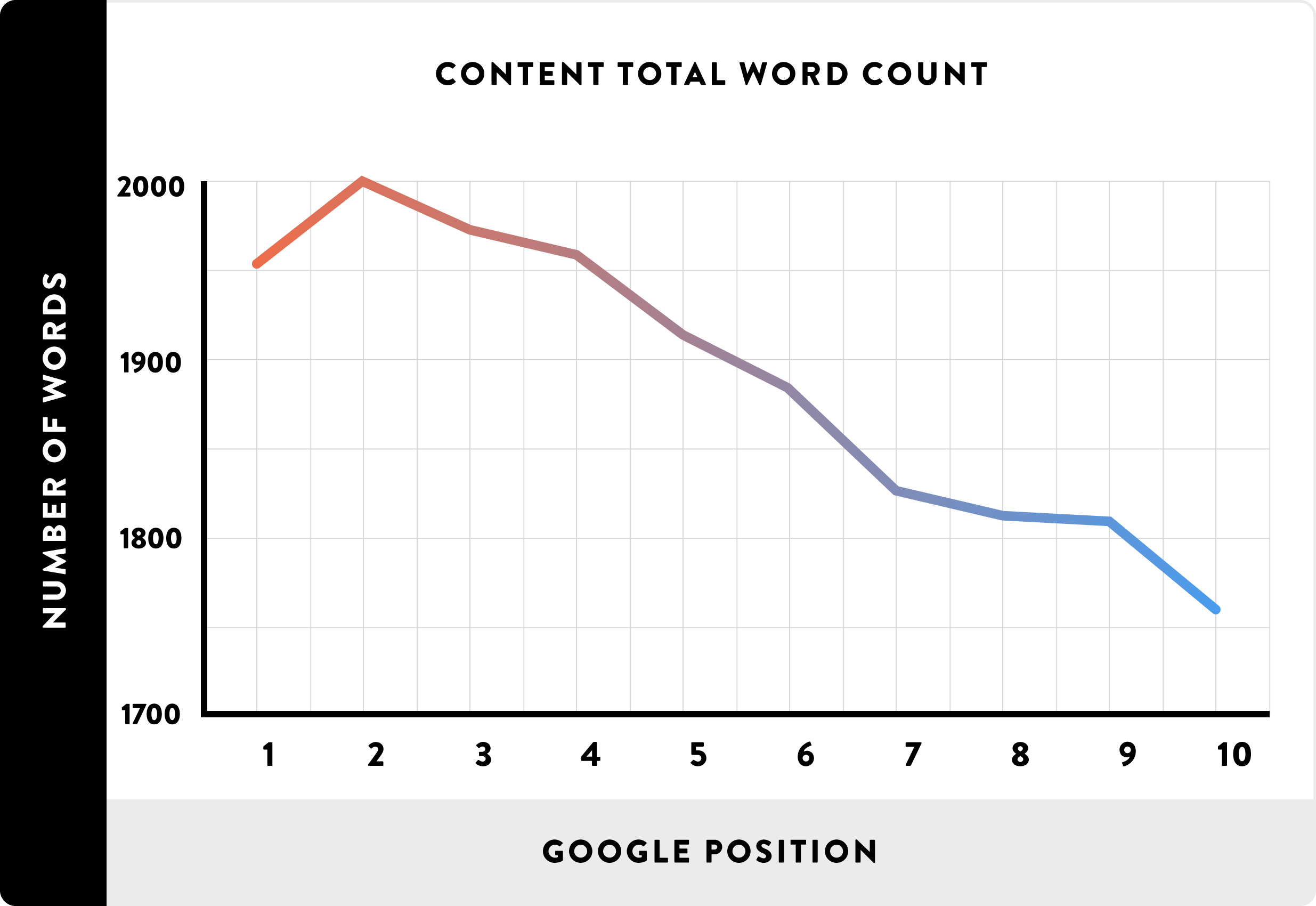
The numbers don’t lie: content that ranks on the first page of Google is between 1750 and 2000 words. Graphs don’t lie, either; check out this telling comparison of number of words on a page versus that page’s Google ranking:
Increase the length of your content. If it makes sense given your industry and the subject matter of the page, target 2000 words. But this isn’t like middle school when you fluffed up your essays and just rambled to hit the word count limit. Quality still wins over quantity. Remember, the reason Google wants to show your content first is because it has been deemed authoritative; search engines think you’re an expert on your subject matter, so prove it. Don’t repeat yourself and keep your thoughts concise, to the point, and sufficiently detailed.
So exactly how do search engines know you’re the expert on…well, whatever you’re an expert on? While there’s no direct method (there is no Google editor reading and interpreting your blog and saying, “Ah! This guy knows his stuff!”), there are lots of indirect methods for gauging the quality of your site. In fact, the way real readers react to your content makes a huge difference. Search engine algorithms factor in the number of repeat visitors to your page, the number of times your page has been bookmarked in a browser, the time a visitor spends on your site, how long it takes them to read to the end of your content, and how often people are searching for your particular brand. User experience metrics like low bounce rates, long dwell times, high number of pages per browsing session are metrics that Google pays attention to. How? Bonus knowledge bomb: Google’s top data ingestion sources include:
- Google Analytics – the most popular piece of javascript appears on 95%+ of sites on the internet and gives them (and you) rich data about your visitors and metrics related to their browsing behavior
- Google Chrome Browser – this is Google’s browser and can send anonymous usage statistics on pages viewed, dwell time, and all browsing behavior to Google’s servers.
- Google Search – includes searches for your brand, clicks to your site in SERPs, and the browsing behavior of those users on your pages
Another way to optimize your content is to use keywords wisely. Keyword stuffing is passe and amateur, and Google will not only detect this technique from a mile away, but will punish you for it. Your keyword(s) should appear within the first 100 words on the page; this helps to establish your content’s topic. Google’s getting smarter at recognizing synonyms, too, so sprinkle some of those throughout your work, just in case.
It’s important to remember that people aren’t just reading content these days. They’re watching videos on YouTube and Vimeo, listening to podcasts on Soundcloud and Spotify, looking for images on Instagram, and looking for short synopses on Twitter. The more multimedia that is intermixed with your content, or the more ways your content is shared on multimedia, the more search engines will like it.
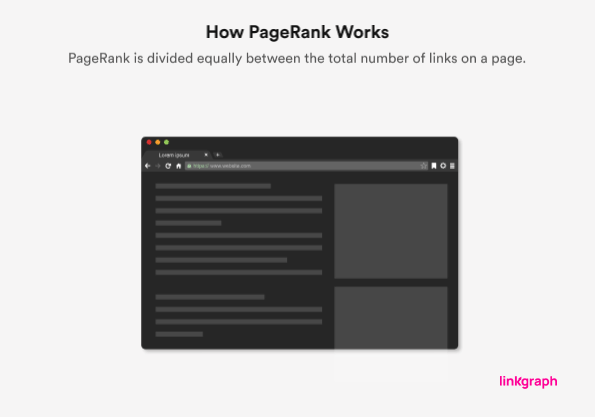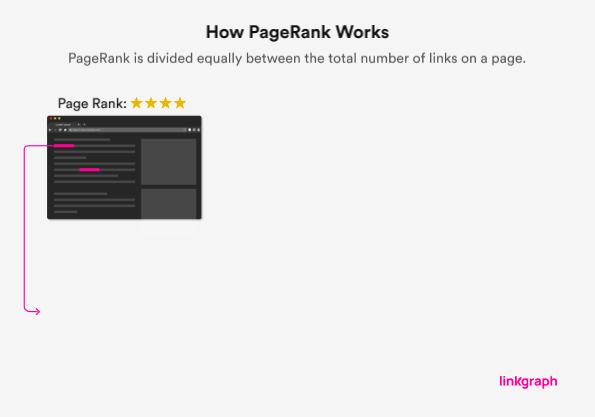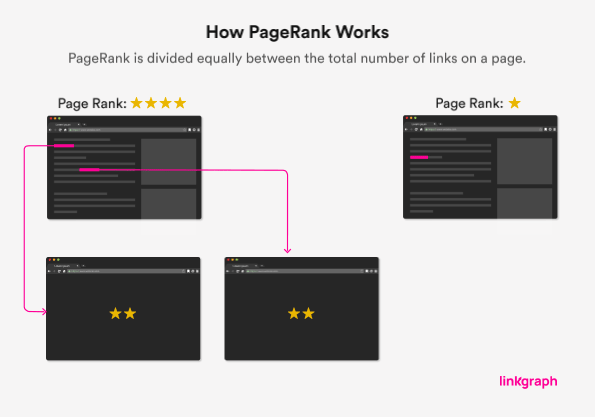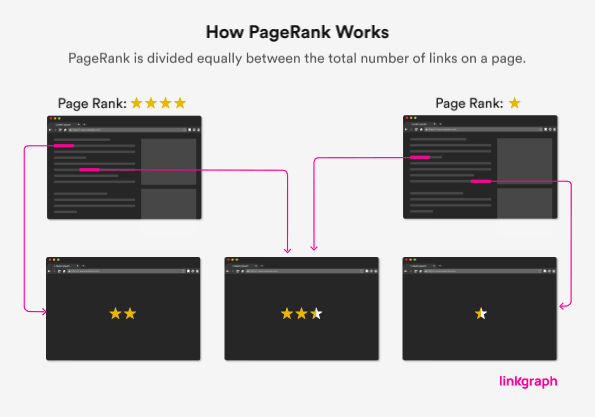
4. Internal Linking
So you’ve created lots and lots of authoritative, high-quality, long-length, multimedia content. Now what? Why, you interlink it, of course! Google analyzes internal links on your website to figure out the relationships between various pages and posts and therefore figure out your content’s importance.
Take a look at your website’s home page. It’s chock-full of great content….but not everything is on your home page (that would definitely spoil the fun). Your home page should be a “pillar page,” or a high-level preview of the other content to be discovered throughout your site. And how will visitors locate that rich bonus content (please don’t say menu, please don’t say menu…)? Yes, through inbound links.
Your home page usually holds the greatest link value within Google’s link algorithm because it usually has–and should have–the most internal links, or backlinks. The link value assigned by the search engine will be shared amongst all of the links on your home page, and that value will be passed onto the page that the link leads to.
Remember this when you post a new blog to your site; add a link on your homepage leading to that new content for added link value and to help Google find it quicker.
Simply put, more links to your site’s related content gives your page more value. “Related” is a key word (not a keyword) here; your internal links should be relevant to both the content on the original page and the content it’s linking to. Please don’t link just for the sake of linking; Google’s on to that, too!
5. Outbound Linking
Now that we understand the importance of internal links, let’s explore outbound links–because you definitely need both to optimize your page. Why? Because while inbound links show that you have tons of awesome, authoritative content on your page and you obviously know your stuff, outbound links help search engines understand that your original work is supported by other work by third parties. This can even serve as an endorsement of sorts.
The same basic principles for quality inbound links apply to outbound links; if you are linking to content outside of your website, be sure that it is relevant, high-quality, and supports your original content. Another best practice for outbound linking for optimization is to use descriptive anchor text. For example, if you’re linking to a statistic about the optimal number of words for your content, include the entire phrase “optimal number of words for your content” in your anchor text, instead of just the single words “number”…or “words.” It’s not necessary to always use keywords in your anchor text (remember–Google’s watching!); the content around your anchor text should be high enough quality to speak for itself.
6. Page and Site Speed
How valuable is your incredibly optimized content if visitors to your site never see it? Not valuable at all. If your page is slow to load, this is exactly what will happen. Users expect pages to load within microseconds; if your page doesn’t, they’ll hit the back button and find what they need somewhere else. Google knows this, and that’s why it incorporates site and page speeds in its algorithms.
Is there a difference in site speed and page speed? Yes and no. Page speed is also known as “page load time,” or the time it takes to display your full page of content. Site speed is actually the time it takes for your pages to load as a user goes through your site, and is a key element of Google’s ranking algorithm. Confused yet? It’s ok. For the sake of this post (about on-page SEO factors), let’s focus today on how to optimize your page speed.
Page speed is one of those invisible pieces of content that we talked about; everything you’ll do to optimize your page speed will take place behind the scenes. Inspect your code for extra scripts, fonts, plug-ins, widgets, or tracking pixels that could have been left behind from earlier versions, reduce the number of page redirects, and compress image sizes to load quickly. Remove excessive images and unnecessary scripts, or anything else that keeps your page from rendering quickly.
Optimizing your pages individually will contribute to the overall optimization of your entire site. Want to check out your page’s load speed? Try Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool; just enter your page’s URL and within seconds Google will evaluate your page’s speed and offer helpful suggestions for optimizing it.
7. Core Meta Tags
Another “behind the scenes” tactic for page optimization is within your metadata. The proper use of title tags, heading tags, and meta tags is a crucial for piece of your overall Google grade, so let’s go through them one-by-one.
Title tag: This is the most important meta tag on your page. Generally, the closer the keyword you want the page to rank for is to the beginning of the title tag, the better. Your title tag for each page should be unique from your other titles, and should adequately describe your page’s content. Bonus tip: adding descriptive modifiers like “2018,” “best,” “guide,” or “top” to your title will help you rank higher in long-tail searches!
Heading tags: Also known as H1, H2, and H3, these tags, along with your title tag and other on-page elements, tell search engines what your page is all about. While the “H’s” go on down to H5, H6, etc., the first three are the most important to your search engine story. The H1 tag is the title of your content as it appears on the page (different from your page title, which is not displayed on the page, paradoxically). Wrapping the beginning and end of your page title with H1s, identifies these words as being super special. Your subtitles are H2s, and H3s are paragraph titles, or other content headers. It might go without saying, but we’ll say it anyway: your header text always should be grammatically correct and contain relevant keywords–but not too many, if you want to avoid the wrath of Google.
Meta description: This is where you really get to flex your writing muscles. Ideally, meta descriptions should be less than 160 characters, include some keywords, concisely describe your page’s content, and be appealing enough that when a portion of your description appears in search engine results, searchers are compelled to click to learn more. Come on, we have faith in you! You can do it!
Alt tag: these should be attached to every meaningful image on your site and help search engines (who don’t have eyes) understand what the images mean.
8. URL Structure and URL Slugs
OK. We’ll get straight to the punchline here: keep your URLs short, simple, descriptive, and free of numerical stuff. The best way to explain this is with examples (you’re welcome!). First, the bad and the ugly.
BAD: site.com/2018/cats/my-favorite-cats/hypoallergenic-cats/cats-with-tails/cats-with-two-eyes/the-cat-from-the-cat-in-the-hat
BAD: site.com/?post=5
BAD: ecommercesite.com/t-shirts/?product_id=5&color=green&size=M
UGLY: site.com/cat-breeds.php
UGLY: site.com/cat-breeds.html
And here are the good:
GOOD: site.com/best-short-hair-cat-breeds-2018
GOOD: ecommercesite.com/t-shirts/dancing-monkey-tshirt
Got it? Good! You don’t want bad or ugly URLs! Remember, you can control your URLs within your site’s settings, and simple, descriptive alias URLs are awesome.
9. Sitemap.XML
Once upon a time, when web crawling was more expensive and bloomfilters used by search robots found more hits than misses, new content discovery was a major problem for search engines. They had to recrawl large percentages of websites looking for new links that they had never indexed before. Included in this were plenty of useless variations of the same pages (HTTP, HTTPS, www, subdomains, query parameters, URL paths with/without trailing slashes all going to the same content) in the hopes of finding new links to crawl so they could fully index the useful and relevant internet. Realizing they needed improved ways for webmasters to surface new pages for their crawlers, they introduced the “sitemap.xml” file for webmasters to provide them a complete source for all of their pages. The rapid proliferation of WordPress sites with sitemaps included out of the box accelerated adoption and made it much easier for them to discover content.
Make sure you’ve got one that has been validated! Feel free to use our free Sitemap.XML checker to make sure your sitemap is following Google’s guidelines. We could write a whole post on the characteristics of a sitemap and how to follow best practices on refresh frequency to optimize your Google Crawl Budget, but we’ll leave that for another time.
10. Robots.txt
Robots.txt are files within our webpages that instruct search engine bots how to crawl your site (it’s a whole robot ecosystem). Just like in the movies, there are good robots (“Danger, Will Robinson!”) and there are bad robots (“I’ll be back.”).
Fortunately, there are more bad robots than good robots. Here are some basic “don’ts” when it comes to robots:
- Always include robots.txt on your site, and never leave it empty
- Don’t let your robots.txt contradict your sitemap
- Never use robots.txt to block access to sensitive information on your site (use password protection instead).
There. Now you have all the tools you need to create the perfectly optimized webpage. Do as much of this as you can, and if you need help with this, especially with off-site link building, drop us a line.
There are several key off-site factors that are very important. Backlinks are important. Content Marketing. Social shares are another metric that reinforces the value of a piece of content in Google’s eyes.